What is hypervisor?
A hypervisor is a piece of software that enables a user to create and runs one or more virtual machines stimultaneously. A hypervisor is also known as the virtual machine monitor (VMM).
One of the key functions that hypervisor provides is isolation, meaning that a guest cannot affect the operation of the host or any other guest, even if it crashes.
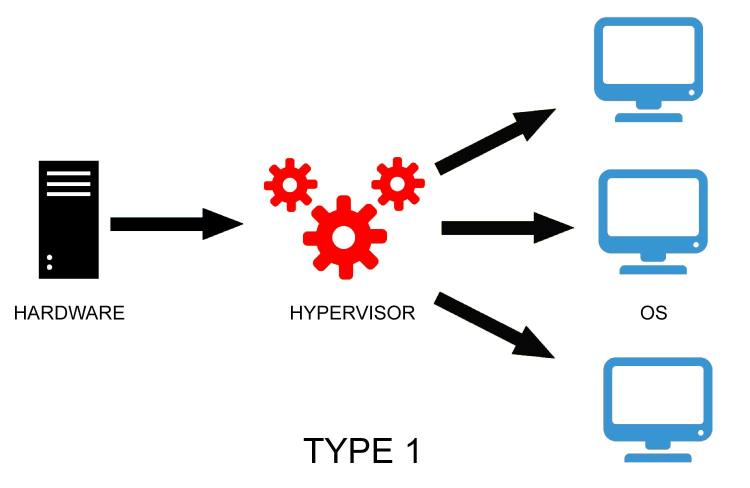
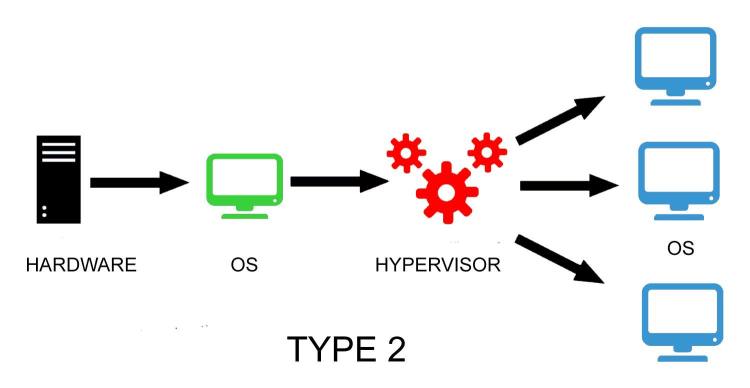
Hypervisors can be of two types: Type 1 and Type 2.
Type 1 – also known as native or bare metal hypervisor, this type of hypervisor runs directly on top of the physical hardware. Each virtual operating system runs atop the hypervisor. Examples of bare metal hypervisors are the Oracle VM server, Vmware ESX/ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.
Type 2 – also known as a hosted hypervisor. This type of hypervisor is installed as a software application on an existing host operating system (OS). Example of the hosted hypervisor are Oracle VirtualBox, Microsoft Virtual PC, Vmware Server and Workstation.
Oracle VirtualBox course
- VirtualBox basics
- What is virtualization?
- What is hypervisor?
- Virtualization benefits
- What is Oracle VM VirtualBox?
- Oracle VirtualBox features
- How Oracle VirtualBox works?
- Executables and components
- Install VirtualBox
- System requirements
- Download Oracle VirtualBox
- Install Oracle VirtualBox on Windows
- Install Oracle VirtualBox on Linux
- Create virtual machines
- What is virtual machine?
- What is guest operating system?
- Create virtual machine
- Install guest OS
- Install Ubuntu
- VirtualBox Guest Additions
- Use virtual machines
- Start virtual machine
- Pause virtual machine
- Virtual Machine snapshots
- Take snapshot
- Restore snapshot
- Delete snapshot
- Clone virtual machine
- Virtual machine groups
- Administer virtual machines
- Change virtual machine name
- Memory managment
- Move virtual machine
- Remove virtual machine
- Log viewer
- Configure devices
- Add DVD or CD-ROM drive
- Add floppy drive
- USB settings
- Virtual disk
- Hard disk controller
- Disk image files
- Configure networking
- Virtual networking
- Network modes
- Configure NAT Networking
- Configure bridged networking
- Configure internal networking
- Configure host-only networking