Manage directories
A directory is a location for storing files on your computer. To be able to administer your Linux distribution, you need to be familiar with commands that create, delete or move directories.
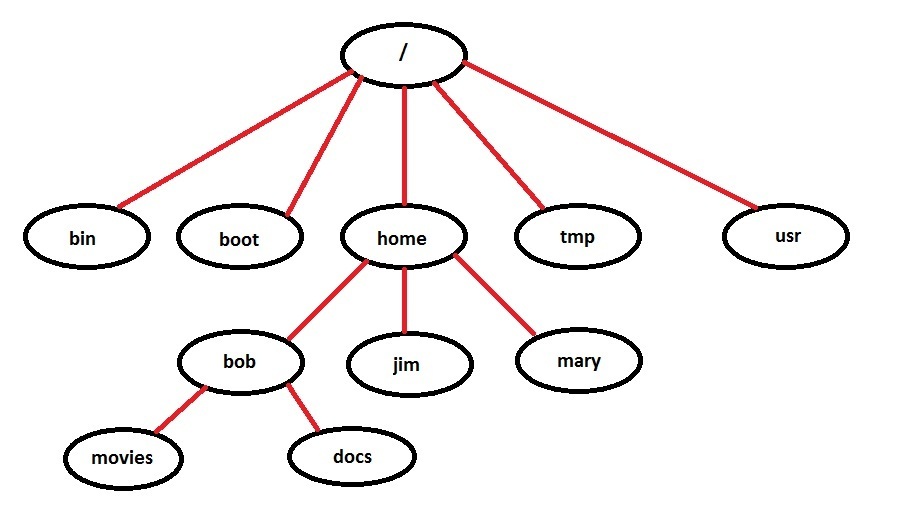
In Linux there is one root directory (represented by a single slash – /), and all files and subdirectories are placed under this directory in a treelike structure:
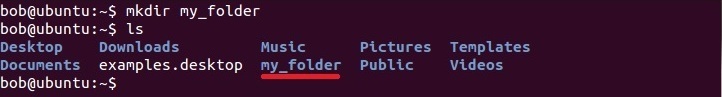
To create a directory, use the mkdir command:
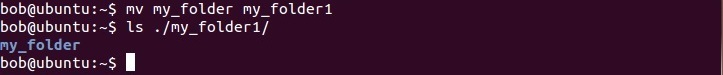
To move a directory, use the mv command with two parameters. The first paramter is the directory that you would like to move and the second paramter is the location where you would like to move the directory to. For example, if you want to move the directory my_folder to /home/bob/my_folder1, you would enter the following command:
To delete a directory, use the rmdir command. There is one problem with this command, though. If you try to delete a non-empty directory, you will get an error:
To avoid this, you need to either empty the directory or use the rm command. If you use the rm command, you need to include the -r option, which means that the command will remove the directory and its content recursively: