User cron jobs
Users can also create their own cron jobs. This is done using the crontab utility (not to be confused with the /etc/crontab configuration file used for system cron jobs). The syntax of the crontab command is:
crontab [-u USER] [OPTIONS] [FILE]
To edit the user’s crontab file, open the crontab editor by running the crontab -e command. This will open up the file in the nano text editor:
The syntax of a cron job is similar to the one described in the previous lesson. You just don’t need to specify the account that will be used to execute the commands, since all commands will be run as the owner of the file. Consider the following line:
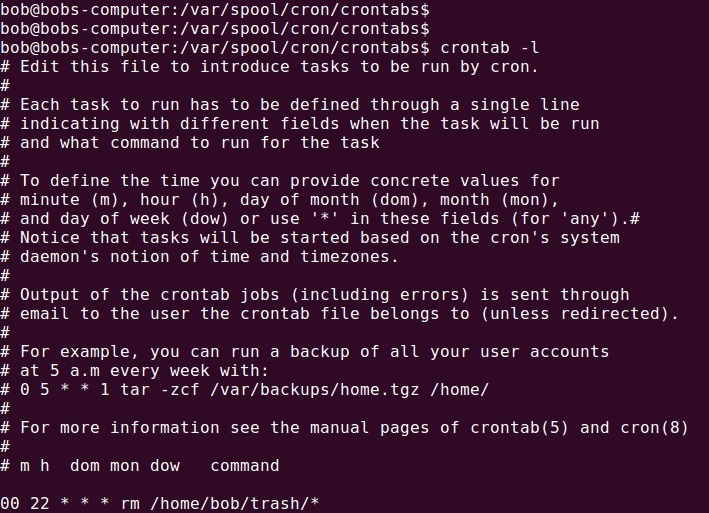
00 22 * * * rm /home/bob/trash/*
The line above specifies that the rm command will be run every day at 22:00.
To display the content of the user’s crontab file, use the -l option:
To remove the current crontab, use the crontab -r command.
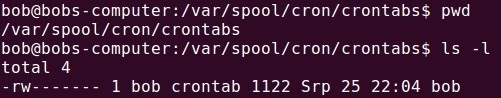
The user crontab files are usually stored in the /var/spool/cron/ directory:
Note that you shouldn’t edit these file directly; use the crontab command instead.