Symbolic links
A symbolic link in Linux is a special type of file that points to other files, instead of pointing to data on the hard drive. Unlike hard links, symbolic links don’t share the same inode number. A symbolic link contains a string that is automatically interpreted and followed by the operating system as a path to another file or directory. A symbolic link is a second file that exists independently of its target.
Symbolic links are more common than hard links. Their biggest advantage is that they can work over different partitions.
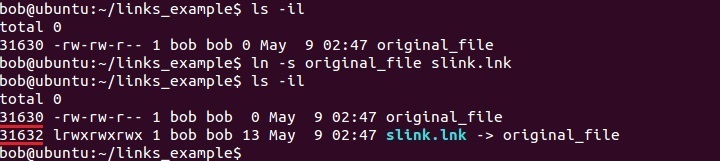
To create a symbolic link, you use the -s option with the ln command, as shown in the example below:
In the picture above you can see that the files don’t have the same inode number.
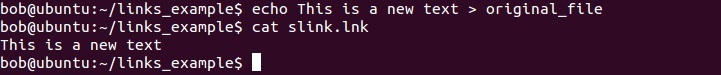
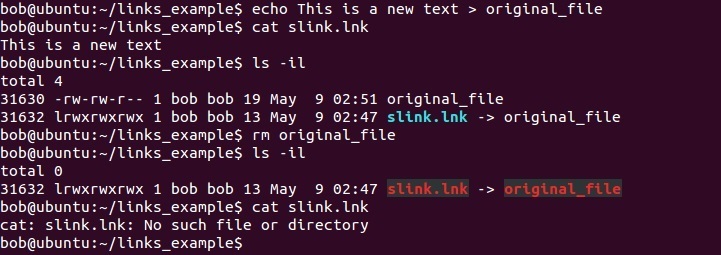
Now we will change the content of the file and then read the new content:
If we delete the original file, the link becomes useless: