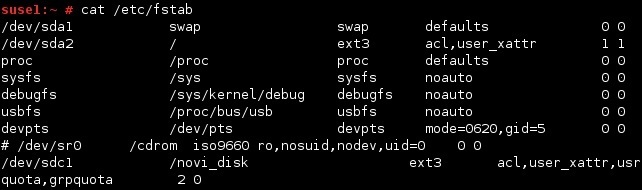
/etc/fstab file
The /etc/fstab file is a system configuration file that contains all available disks, disk partitions and their options. Each file system is described on a separate line. Each line contains six fields separated by one or more spaces or tabs. If you add a new hard disk or have to repartition the existing one, you’ll probably need to modify this file.
The /etc/fstab file is used by the mount command, which reads the file to determine which options should be used when mounting the specified device.
Here is a sample /etc/fstab file:
As you can see from the output above, each line consists of six fields. Here is a description of each of them:
- Device – the first field specifies the mount device. These are usually device filenames. Most distributions now specify partitions by their labels or UUIDs.
- Mount point – the second field specifies the mount point, the directory where the partition or disk will be mounted. This should usually be an empty directory in another file system.
- File system type – the third field specifies the file system type.
- Options – the fourth field specifies the mount options. Most file systems support several mount options, which modify how the kernel treats the file system. You may specify multiple mount options, separated by commas.
- Backup operation – the fifth field contains a 1 if the dump utility should back up a partition or a 0 if it shouldn’t. If you never use the dump backup program, you can ignore this option.
- File system check order – the sixth field specifies the order in which fsck checks the device/partition for errors at boot time. A 0 means that fsck should not check a file system. Higher numbers represent the check order. The root partition should have a value of 1 , and all others that need to be checked should have a value of 2.
Consider the following line from our sample /etc/fstab file:
This line specifies that the partition /dev/sdc1 should be mounted on /novi_disk. The partition should be formatted with ext3. The mount, dump and fsck options are also specified.
Geek University recommends the following video course to get you started with Linux.