Create a log entry
To manually create a log entry in Linux, you can use the logger command. This command serves as an interface to the syslog system log module and it is commonly used in scripts. For example, a backup script might use the logger command to record details such as its start and stop times and the number of files it has backed up.
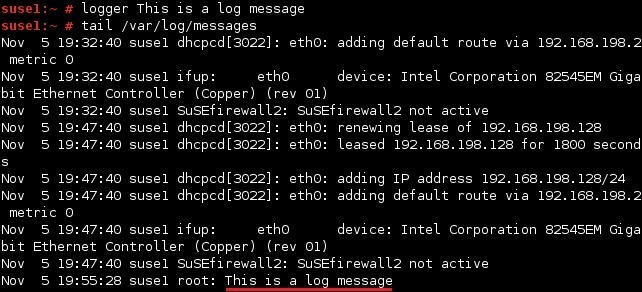
Here is a simple example:
By default, logger writes to /var/log/messages.
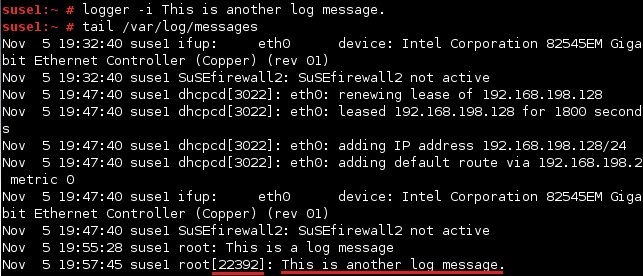
To record the process ID (PID) of the logger process along with other data, use the -i option:
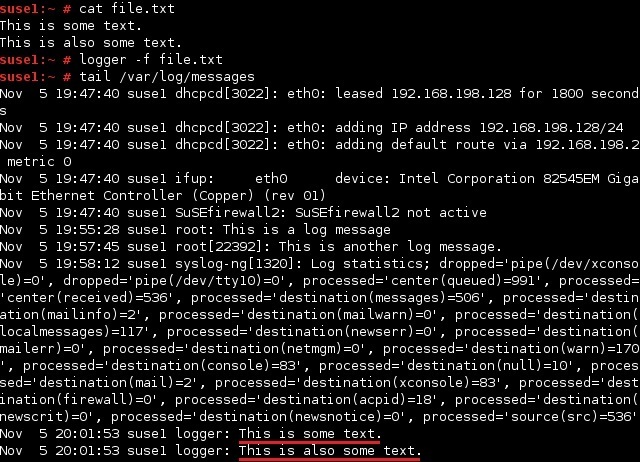
To log the content of a file, use the -f option:
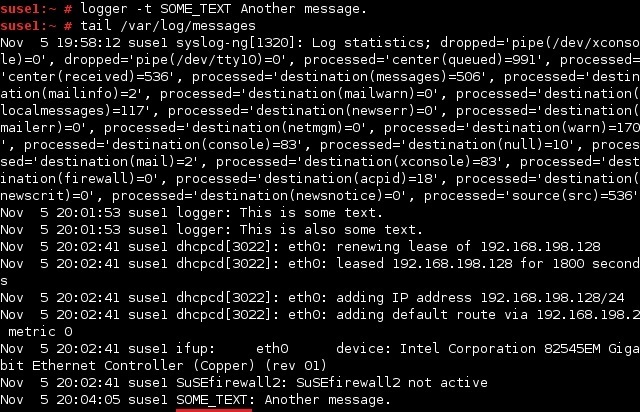
By default, logger includes its name in the log file as the tag. To change the tag, use the -t TAG option:
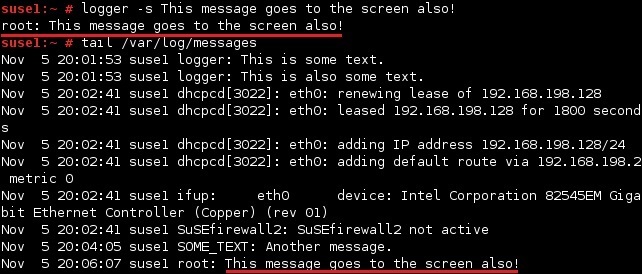
To echo the message to standard error (the screen), as well as to /var/log/messages, use the -s option: