Change runlevel
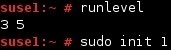
The init process is the first process that is run by the kernel. Its primary purpose is to start processes from a script stored in the /etc/inittab file. You can use the init command to reread this file or change to a new runlevel. For example, to change from your current runlevel to runlevel 1 (the single-user mode), you can use the init 1 command:
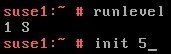
Your system should reach the runlevel 1. To get back to the multiuser GUI mode, you can use the init 5 command.
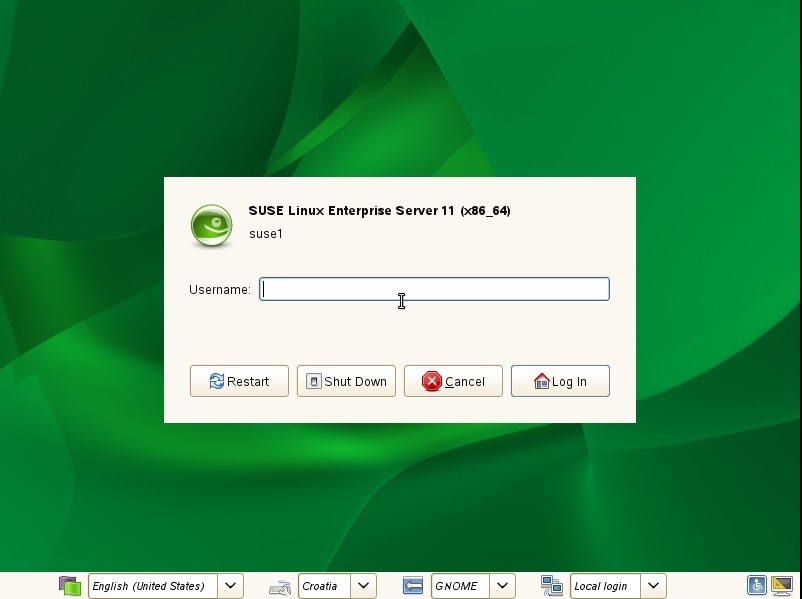
You should be back in the GUI mode:
Here is a brief description of the runlevels in Linux you can reach using the init command. Note that the values listed below do not apply to all Linux distributions:
- 0 – shuts down the system.
- 1, s, or S – single-user mode. Limited number of services are started. Usually used for system maintenance.
- 2 – text mode with multiple users, but without the network support.
- 3 – text mode with multiple users and networking.
- 4 – usually not defined.
- 5 – the default runlevel. Multiuser GUI. The most common runlevel for Linux workstations.
- 6 – reboots the system. Used to restart a machine in the default runlevel.