What is DHCP?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network protocol used to assign various network parameters to a device. DHCP greatly simplifies administration, since there is no need to assign static network parameters for each device separately.
DHCP is a client-server protocol. A client is a device that is configured to use DHCP. When a client boots up, it sends a broadcast message in search of a DHCP server. DHCP server maintains a pool of available IP addresses and offers one of them to the host. A DHCP server can also provide some other parameters, such as:
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- domain name
- DNS server
Linux can be used as both DHCP client and DHCP server.
Here is a description of the DHCP process:
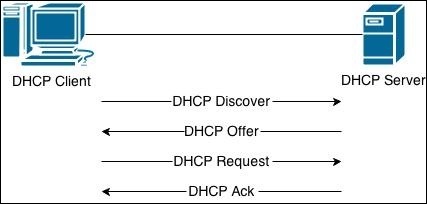
DHCP client goes through the four step process:
1. a DHCP client sends a broadcast packet (DHCP Discover) to discover DHCP servers on the LAN segment.
2. the DHCP servers receive the DHCP Discover packet and respond with DHCP Offer packets, offering IP addressing information.
3. if the client receives the DHCP Offer packets from multiple DHCP servers, the first DHCP Offer packet is accepted. The client responds by broadcasting a DHCP Request packet, requesting network parameters from a single server.
4. the DHCP server approves the lease with a DHCP Acknowledgement (DHCP Ack) packet. The packet includes the lease duration and other configuration information.