What is a guest operating system?
A guest operating system is an operating system installed inside a virtual machine. A guest operating system can be different from the host operating system (for example, you can run a Linux distribution in VMware Player installed on a Windows machine).
Many guest operating systems are supported by VMware Player, such as Windows 98, Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012, Solaris, Debian, CentOS, SUSE, FreeBSD, Red Hat, etc. To see the full list of the supported guest operating systems, go to this link. VMware Player is not listed, but the information for Workstation is applicable to Player.
Just like with the operating system installation on a physical computer, you need to have an installer disc or an ISO image file of the operating system you would like to install. An ISO file (also called an ISO image) is a single file that replicates the contents of an optical disc. ISO files are used to distribute large programs over the Internet, including operating systems such as Microsoft Windows or Linux. For example, here you can download an ISO version of Damn Small Linux and use it to install this Linux distribution in VMware Player:
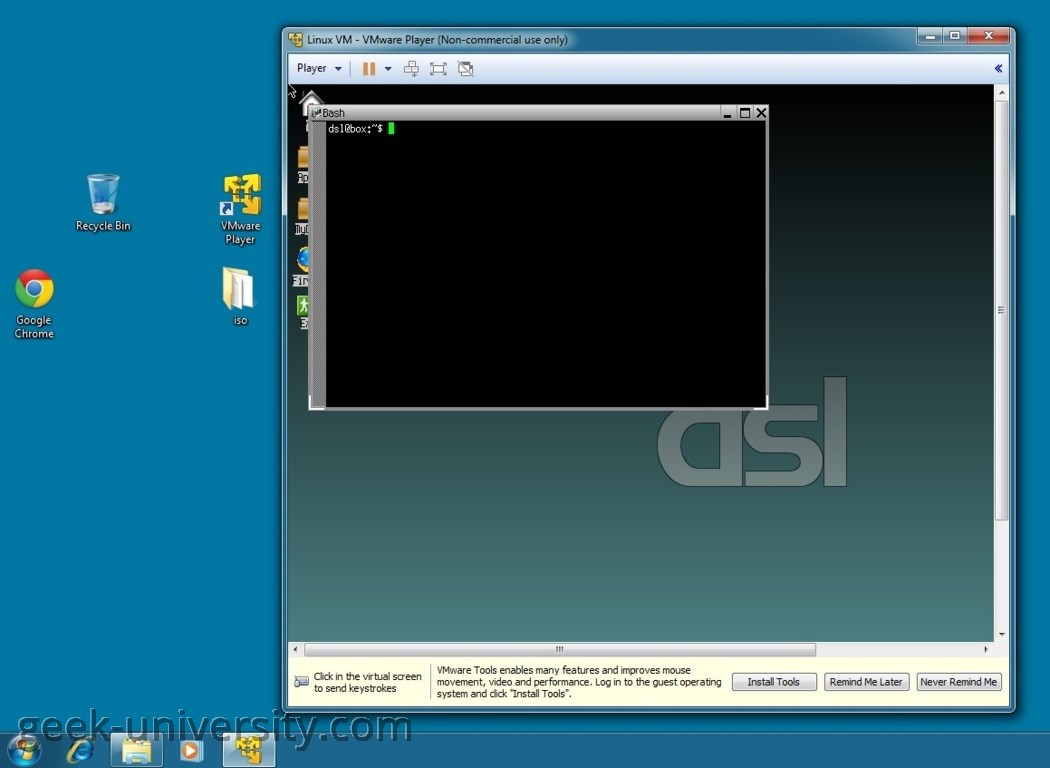
In the picture above you can see that we are running Damn Small Linux (the guest operating system) inside VMware Player installed on Windows 7 (the host operating system).
VMware Player Course
- Introduction
- VMware Player overview
- System requirements for VMware Player
- VMware Player download
- Install VMware Player on Windows
- Install VMware Player on Linux
- Create virtual machines
- What is a virtual machine?
- What is a guest operating system?
- Create a virtual machine
- Manually install a guest operating system
- Easy Install feature in VMware Player
- VMware Tools overview
- Install VMware Tools in Windows
- Install VMware Tools in Linux
- Virtual machine files
- Use virtual machines
- Start a virtual machine
- Suspend a virtual machine
- Drag-and-Drop feature
- Copy and Paste feature
- Shared folders overview
- Enable a shared folder for a virtual machine
- Connect a USB device to a virtual machine
- Connect USB HIDs to a virtual machine
- What is Unity Mode?
- Use Unity Mode
- Manage virtual machines
- Change the virtual machine name
- Change the guest operating system version
- Change the working directory of a virtual machine
- Change the memory allocation
- Move a virtual machine
- Configure a virtual machine for compatibility
- Universal Unique Identifier (UUID)
- Delete virtual machines
- VMware Player log files
- Configure devices
- Add a CD-ROM drive
- Add a floppy drive
- Configure Legacy Emulation Mode
- Configure a USB Controller
- Add a USB controller
- Enable isochronous USB devices
- What is a virtual disk?
- Configure a virtual hard disk
- Add a new virtual hard disk
- Add an existing virtual hard disk
- Compact a virtual hard disk
- Expand a virtual hard disk
- Defragment a virtual hard disk
- Remove a virtual hard disk
- Add a virtual parallel port
- Add a virtual serial port
- Add a generic SCSI device
- Virtual SMP (Symmetric Multi-Processing)
- Enhanced virtual keyboard feature
- Configure networks
- Virtual networking components
- Networking configurations
- Add a virtual network adapter
- Configure bridged networking
- Configure NAT networking
- Configure host-only networking