Admission Control policy
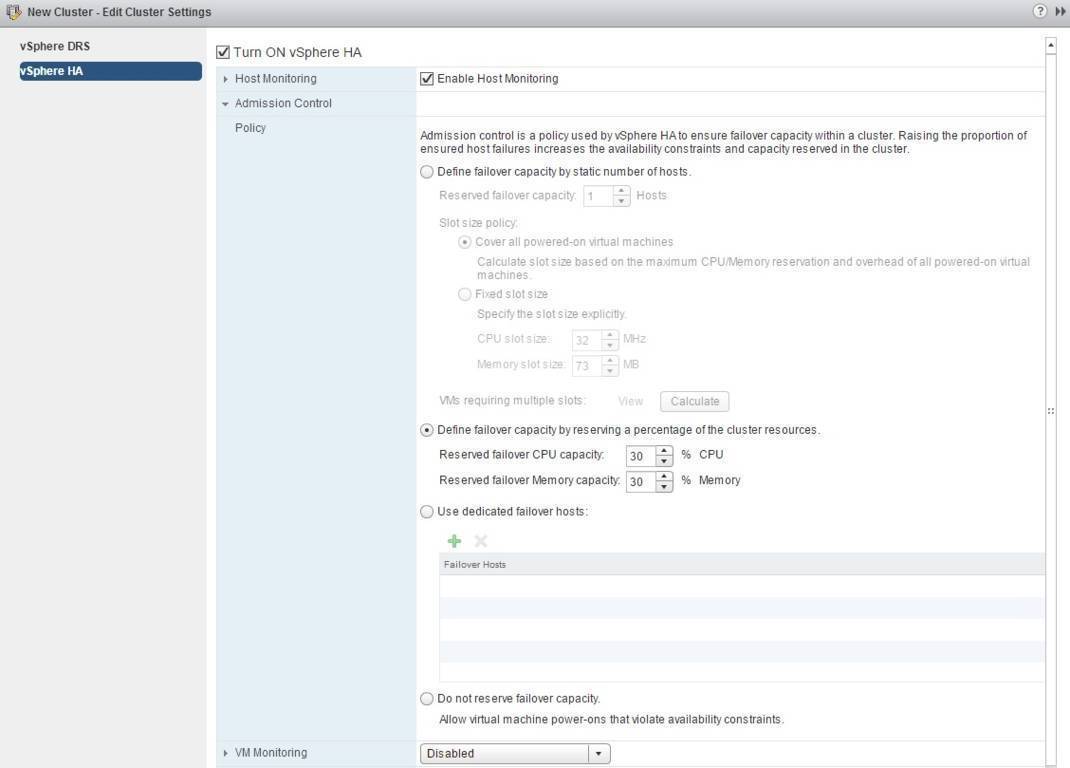
You can choose between these four policies to define how Admission Control will ensure capacity for the cluster:
- Define failover capacity by static number of hosts – a number of hosts that may fail is specified. Spare capacity is calculated using a slot-based algorithm. A slot represents the amount of memory and CPU assigned to powered-on virtual machines. This option is recommended in vSphere environments that have VMs with similar CPU and memory reservations.
- Define failover capacity by reserving a percentage of the cluster resources – a percentage of the cluster’s aggregate CPU and memory resources that will be reserved for recovery from ESXi host failures is specified. The specified percentage indicates the total amount of resources that will remain unused for vSphere HA purposes. This option is recommended in vSphere environments that have VMs with highly variable CPU and memory reservations.
- Use dedicated failover hosts – one or more hosts are used exclusively for failover purposes. The failover hosts cannot have powered-on virtual machines, because they are used for failover purposes only.
- Do not reserve failover capacity – VMs can be powered on, even if the availability constraints are violated. This option basically disables Admission Control.
You can configure Admission Control using vSphere Web Client. Select your cluster from the inventory, go to Manage > Settings > vSphere HA and click on the Edit button on the right:
The Edit Cluster Settings dialog box opens. Check the Admission Control checkbox and expand the panel. This should open up the Admission Control Policy window. In our example, we will use the Define failover capacity by reserving a percentage of the cluster resources option to reserve 30% of the cluster’s CPU and memory resources for failover purposes: