Virtual Machine File System (VMFS)
VMFS (Virtual Machine File System) is a clustered file system from VMware that provides storage virtualization. VMFS offers many virtalization-based features, such as:
- concurrent access to shared storage. Multiple ESXi hosts can read and write to the same storage device at the same time.
- encapsulation of virtual machine’s files in directories.
- automatic restart of a failed VM on another ESXi host.
- migration of powered-on virtual machines from one ESXi host to another without downtime.
- clustering of VMs accross different physical servers.
- VMFS datastore size can be increased while VMs residing on the datastore are running.
- when combined with shared storage, advanced vSphere features such as vMotion, DRS, HA, and FT are supported.
- support for thin-provisioned VMDK files, which allows VMFS datastores overallocation.
- support for RDM (Raw Device Mapping) devices.
VMFS can be created on three types of SCSI-based storage systems: direct-attached storage, FC storage, and iSCSI storage. A virtual disk stored on a VMFS datastore will appear to the virtual machine as a mounted SCSI device. The operating system running inside the VM will see its native file system, not VMFS.
The current VMFS version is VMFS-5. This version uses 1MB block size and can support VMDK files of up to 62TB. You can have up to 256 VMFS datastores per host, with the maximum size of 64TB.
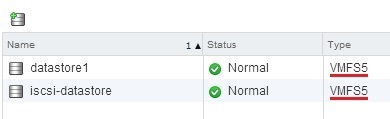
In the picture above you can see that both datastores are using VMFS-5 as the file system.