Roles explained
In vSphere, roles are collections of privileges that enable users to perform tasks such as power on a virtual machine, configure a network, create an alarm, etc. ESXi comes with three built-in roles:
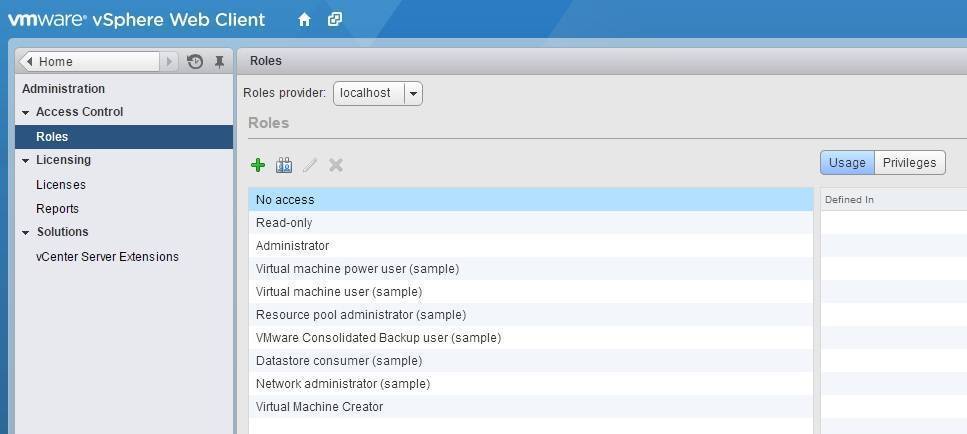
- No access – prevents access to an object or objects in the inventory. For example, if a user is granted permissions on the ESXi host but should be prevented from accessing a specific VM, you could use the No access role on that specific VM.
- Read-only – allows a user to only see the objects in the vSphere Client inventory, but prevents a user from taking any action on the objects. For example, a user with the Read-only role would be able to see a list of VMs in the inventory but could not power them on or off.
- Administrator – gives a user the full authority over an object.
The three roles described above are permanent, meaning that they cannot be modified in any way. There are also six default sample roles that can be used as is or as guidelines for creating custom roles. These roles are:
- Virtual machine power user
- Virtual machine user
- Resource pool administrator
- VMware consolidated backup user
- Datastore consumer
- Network administrator
You can display the list of roles using vSphere Web Client. On the Home screen, select Administration > Roles:
A role can be assigned to a user or a group.