Directory management
As you probably know, a directory is a file that stores other files. In Raspbian (and Linux in general), all files are stored under the root directory (represented by the slash (/) character) in a tree-like structure. In this section, we will describe some basic commands used to manage directories in Raspbian.
Create a directory
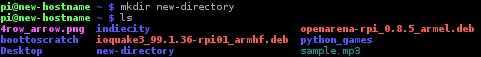
The mkdir command is used to create a directory:
Move a directory
To move a directory, the mv command is used. Two parameters need be specified: the first paramter is the directory you would like to move and the second parameter is the location where you would like to move the directory to. For example, if we want to move the directory named new-directory located at /home/pi/ to /tmp/, we need to enter the following command:
Delete a directory
The rmdir command is used to delete a directory. For example, to delete the directory new-directory located at /tmp/, the following command needs to be used:
If you get the rmdir: failed to remove ‘/tmp/new-directory/ ‘: Directory not empty error, it means that your directory contain files. To remove the directory along with the content of the directory, use the rm command with the -r option:
Copy a directory
To copy a directory, use the cp command with the -r flag and two parameters: the source directory you would like to copy and the destination. For example, to copy the /home/pi/new-directory to the /tmp/ directory, use the following command: