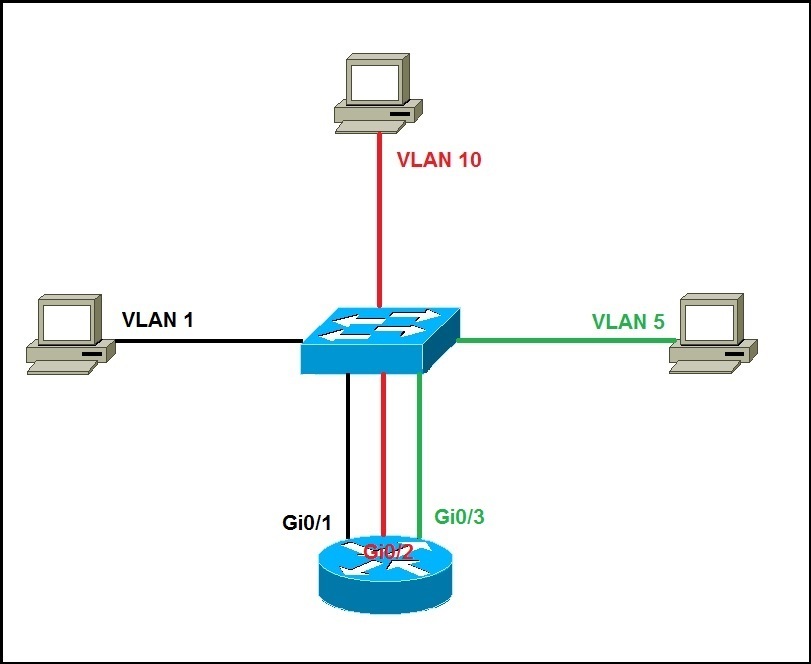
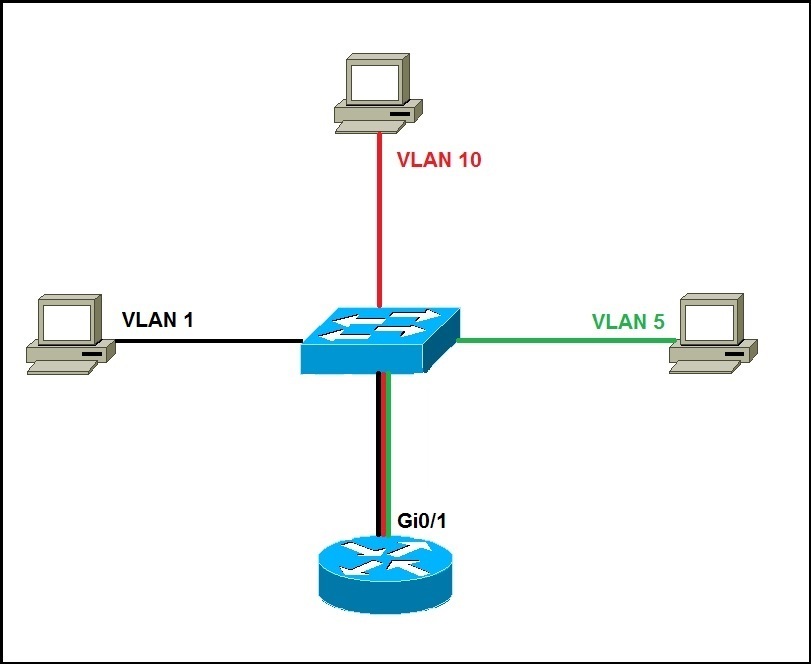
Routing between VLANs
Each VLAN is its own subnet and broadcast domain, which means that frames broadcast onto the network are only switched between the ports within the same VLAN. For inter-VLAN communication, a layer 3 device (usually a router) is needed. This layer 3 device needs to have an IP address in each subnet (VLAN) and have a connected route to each of those subnets. The hosts in each subnet can use the router’s IP addresses as their default gateway.
Three options are available for routing between VLANs:
1. Use a router, with one router LAN interface connected to the switch for each and every VLAN. Since you need one Ethernet interface on your router to connect to each VLAN, this option is not really scalable and rarely used today.
2. Use one router interface with trunking enabled. This option is called router on a stick (ROAS) and allows all VLANs to communicate through a single interface.
3. Use a Layer 3 switch, a device that performs both the switching and routing operations.