Domain Name Service (DNS)
Domain Name Service (DNS) is an application layer protocol used to resolve hostnames to IP addresses. Although a host can be accessed by using only its IP address, DNS makes your life easier by using domain names. For example, you can access the Google website by typing http://208.117.229.214 in your browser, but it is much easier to type http://www.google.com.
Each host that wants to use DNS needs to have a DNS server configured. When you type a URL in your browser (e.g. http://www.google.com), your host will query the DNS server for the IP address of www.google.com. The DNS server will resolve the query and send the answer back to the host. The host will then be able to establish a connection to http://www.google.com.
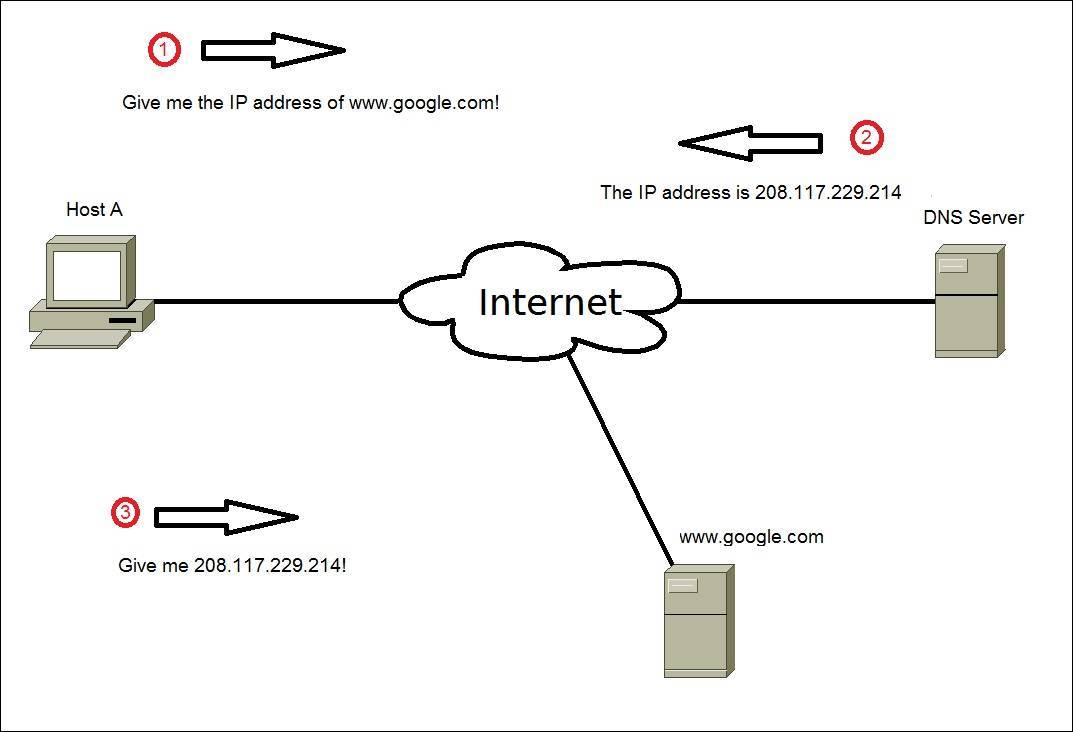
Consider the following example:
1. The user enters www.google.com in his browser. The host needs to know the IP address of www.google.com in order to establish a network connection. The host sends a DNS query to its DNS server, looking for the IP address of www.google.com.
2. The DNS server sends a reply back to the host, listing the IP address of 208.117.229.214 as www.google.com’s IP address.
3. The host can establish a network connection to the web server hosting www.google.com.