What is Cisco ACS?
Cisco Access Control Server (ACS) is an authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) platform that lets you centrally manage access to network resources for a variety of access types, devices, and user groups. It is used for the following purposes:
- device administration – authenticates administrators, authorizes commands, and provides accounting functions.
- remote access – it can work with remote network access devices to enforce access policies.
- wireless – authenticates and authorizes wireless users and hosts and enforces wireless policies.
- network admission control – communicates with posture and audit servers to enforce admission control policies.
ACS is usually used to centrally manage the users and control what they are authorized to do. Users are created locally on the ACS server and the routers and switches are configured to use ACS for authentication and authorization. This way, you can avoid creating the same users locally on every router and switch in your network. ACS server can also use an external user database (such as Microsoft Active Directory) for authentication purposes.
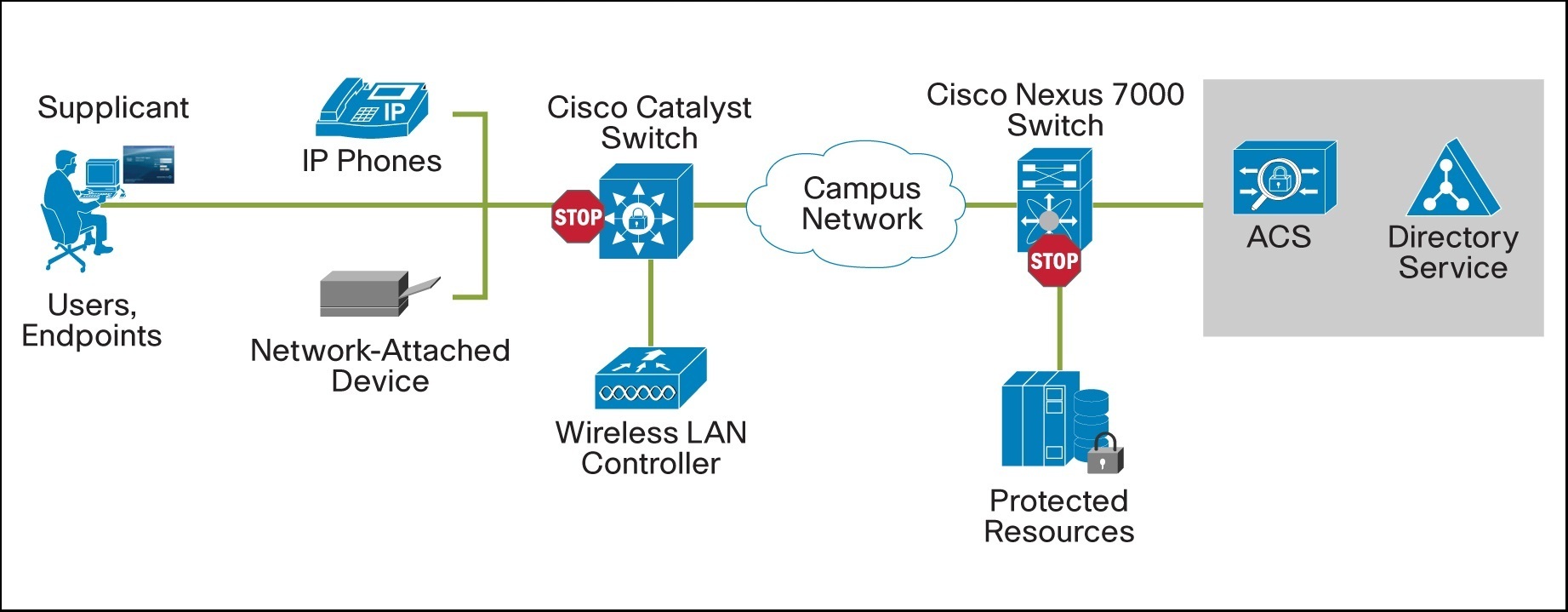
An example ACS deployment scenario can be seen in the picture below (image source: Cisco):
Cisco ACS comes in three flavours:
- hardware appliance – a physical appliance that can be purchased from Cisco. The appliance comes with the ACS software preinstalled.
- application on a Windows server – a software package installed on a Windows system.
- a dedicated virtual machine – ACS running in a virtual machine.
Here is a picture of the hardware appliance (image source: Cisco):