What is a router?
A router is a network device that connects different computer networks by routing packets from one network to the other. This device is usually connected to two or more different networks. When a data packet comes to a router port, the router reads the address information in the packet to determine out which port the packet will be sent. For example, a router provides you with the internet access by connecting your LAN with the Internet.
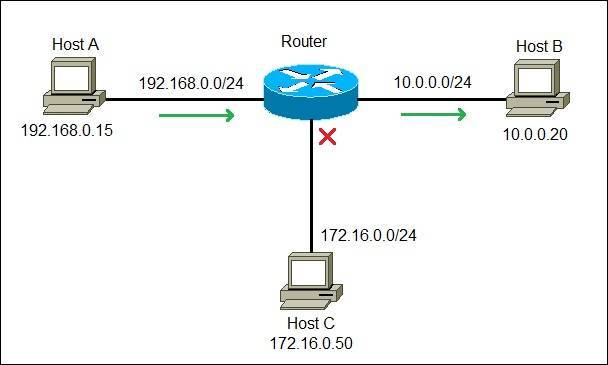
A router is considered a Layer 3 device of the OSI model because its primary forwarding decision is based on the information of the OSI Layer 3 (the destination IP address). If two hosts from different networks want to communicate with each other, they will need a router between them. Consider the following example:
We have a network of three computers. Note that each computer is on a different network. Host A wants to communicate with Host B and sends a packet with Host B’s IP address (10.0.0.20) to the default gateway (the router). The router receives the packet, compares the packet’s destination IP address to the entries in its routing table and finds a match. It then sends the packet out the interface associated with that network. Only Host B will receive the packet. In fact, Host C will not even be aware that the communication took place.