traceroute command in IOS
The traceroute command in Cisco IOS is used to identify the path used by a packet to reach its target. It identifies the routers in the path from the source host to destination host and it can be useful when troubleshooting network problems. Using this command you can figure out which router in the path to an unreachable target should be examined more closely as the probable cause of the network’s failure.
Consider the following example:
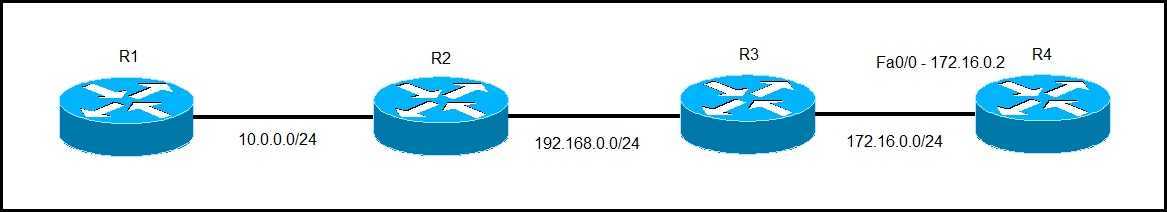
In the picture above we have a network of four routers. The network is functional. Consider what happens when we issue the traceroute command on R1 to the IP address of the router R4 Fa0/0 interface (172.16.0.2):
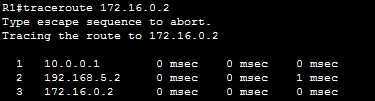
You can see that the traceroute command has listed the IP addresses of all of the routers in the path. Now consider what happens if R3 fails:
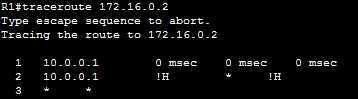
Note that there is no response from R3 (192.168.5.2). Using this information, we can assume that there is a problem with R3 and investigate the matter. The !H in the output indicates that the host is unreachable. Other character that can appear in the traceroute output are:
- number of miliseconds – the round-trip time in milliseconds.
- * – the probe has timed out.
- A – administratively prohibited (for example, with an access-list).
- Q – source quench (the destination is too busy).
- I – user interrupted test.
- U – port is unreachable.
- N – the network is unreachable.
- P – the protocol is unreachable.
- T – timeout.
- ? – unknown packet type.