Frame tagging explained
Frame tagging is used to identify the VLAN that the frame belongs to in a network with multiple VLANs. The VLAN ID is placed on the frame when it reaches a switch from an access port, which is a member of a VLAN. That frame can then be forwarded out the trunk link port. Each switch can see what VLAN the frame belongs to and can forward the frame to corresponding VLAN access ports or to another VLAN trunk port.
Two trunking protocols are usually used today for frame tagging:
- Inter-Switch Link (ISL) – Cisco’s proprietary VLAN tagging protocol.
- IEEE 802.1q – IEEE’s VLAN tagging protocol. Since it is an open standard, it can be used for tagging between switches from different vendors.
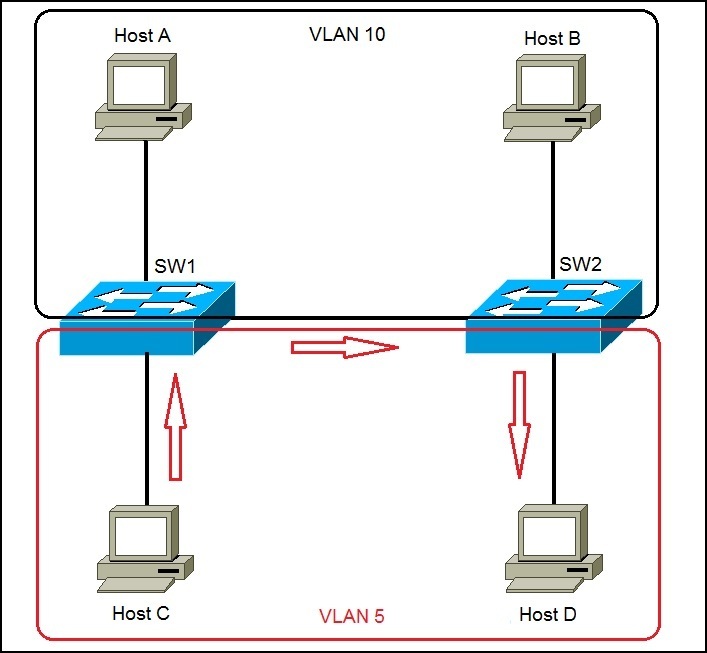
Consider the following example to understand the concept of frame tagging:
There are two VLANs in the toplogy pictured above: VLAN 5 and VLAN 10. Host C sends a broadcast packet to switch SW1. Switch SW1 receives the packet, tags the packet with the VLAN ID of 5 and sends it to SW2. SW2 receives the packet, looks up at the VLAN ID, and forwards the packet only out the port in VLAN 5. Host A and host B will not receive the packet because they are in different VLAN (VLAN 10).