Broadcast domain explained
The term broadcast domain is used to describe a group of devices on a specific network segment that can reach each other with Ethernet broadcasts. Broadcasts sent by a device in one broadcast domain are not forwarded to devices in another broadcast domain. This improves the performance of the network because not all devices on a network will receive and process broadcasts.
Routers separate a LAN into multiple broadcast domains (every port on a router is in a different broadcast domain). Switches (by default) flood Ethernet broadcast frames out all ports, just like bridges and hubs. All ports on these devices are in the same broadcast domain.
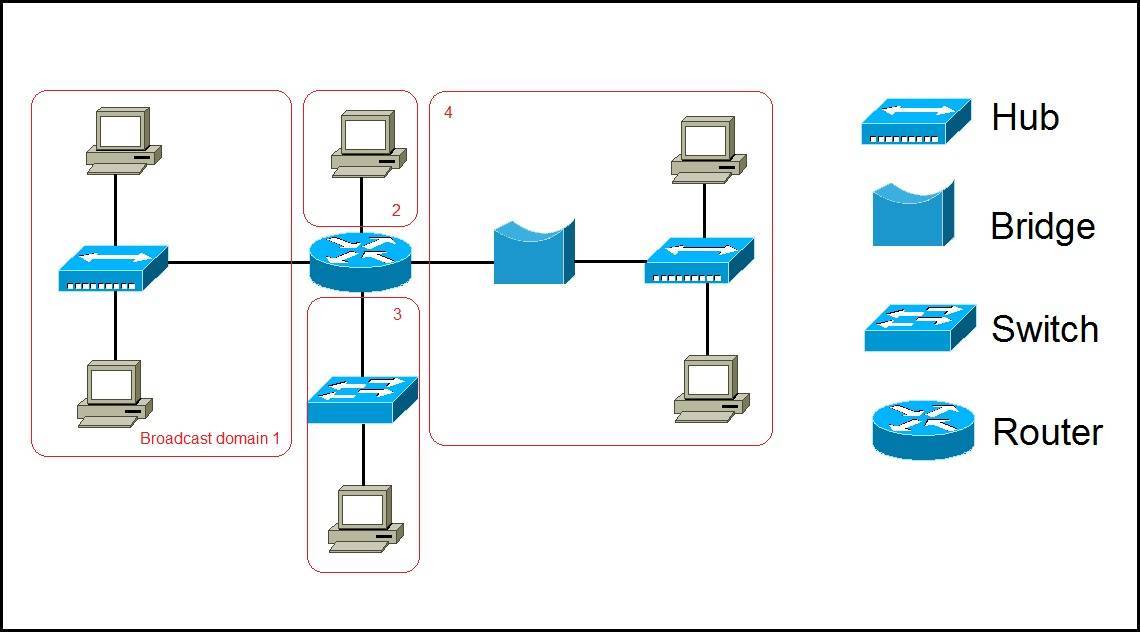
To better understand the concept of broadcast domains, consider the following example:
In the picture above we have a network of six computers, two hubs, a bridge, a switch, and a router. The broadcast domains are marked in red. Remember, all devices connected to a hub, a bridge, and a switch are in the same broadcast domain. Only routers separate the LAN into multiple broadcast domains. That is why we have four broadcast domains in the network pictured above.