Configuration files
The Apache HTTP Server is configured by placing directives in plain text configuration files. The location of the configuration files depends on the operating system version. Historically, the main Apache configuration file was called httpd.conf. However, on Ubuntu, the main configuration file is apache2.conf. In this section we will describe the main configuration files found in Ubuntu.
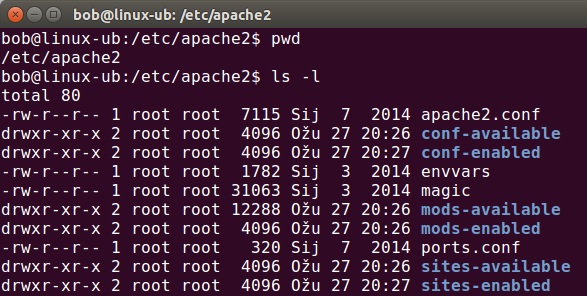
In Ubuntu, the Apache configuration files are stored in the /etc/apache2 directory:
Here is a brief description of the files in this directory:
- apache2.conf – the main Apache2 configuration file that contains settings global to Apache.
- conf-available – a directory that contains available configuration files.
- conf-enabled – a directory that holds symlinks to the files in /etc/apache2/conf-available.
- envvars – a file where Apache environment variables are set.
- magic – a text file that instructions for determining MIME type based on the first few bytes of a file.
- mods-available – a directory that contains configuration files to both load modules and configure them.
- mods-enabled – a directory that holds symlinks to the files in /etc/apache2/mods-available.
- ports.conf – a configuration file that houses the directives that determine the TCP ports Apache is listening on.
- sites-available – a directory that has configuration files for Apache Virtual Hosts. Virtual Hosts allow Apache2 to be configured for multiple sites that have separate configurations.
- sites-enabled – a directory that contains symlinks to the /etc/apache2/sites-available directory.